Serial vs Parallel Programs
Serial vs Parallel Programs
Understanding how programs can utilize multiple cores…
helps us to understand how to use the HPC effectively.
Serial Program
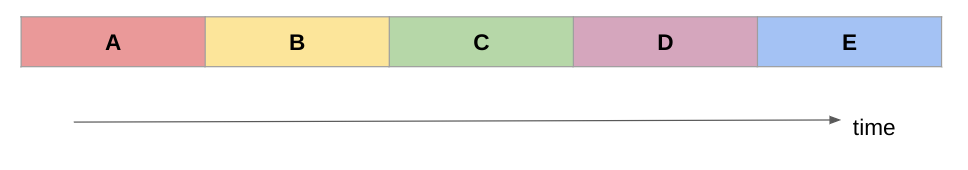
Serial program schematic
- Serial problems use a single CPU core
- Solve a series of problems one after the other
- Each stage of the calculation (A, B, C…) may depend on the output of the previous stage, or they may be independent (and so could run in any order)
Parallel Program
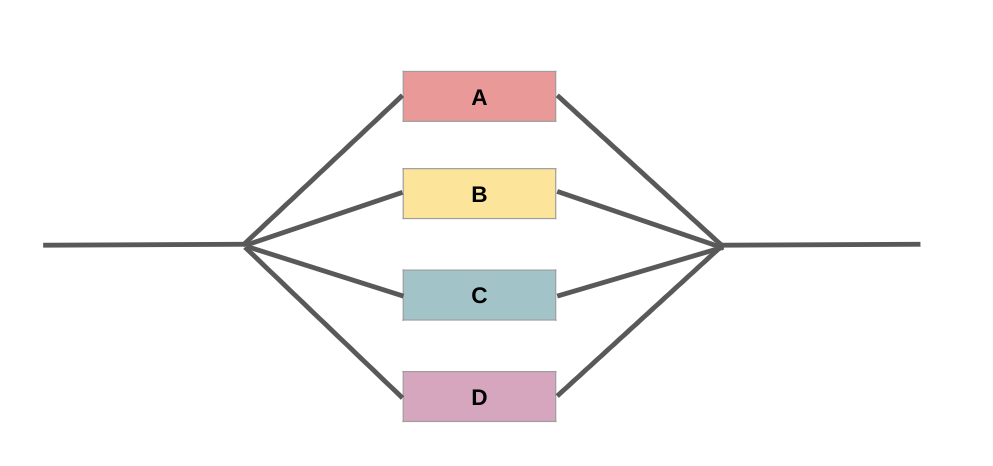
Parallel program schematic
In contrast: problems can be solved simultaneously on multiple cores
Parallel Program

Parallel program schematic
- All the stages (A, B, C…) are independent of each other and do not require one stage to be completed before another stage begins
- “Perfectly parallel” or “embarrassingly parallel” because it is a task that is “embarrassingly easy” to split up into parallel tasks
Imperfectly Parallel
Most tasks you run or models you run on the HPC will fall somewhere in-between serial and parallel:
- Certain sections of the code will be able to be parallelised while other sections will rely on the output of the previous stage and so need to be serialised
- You can express how much of your work is parallelised with a rough percentage
- The higher the parallel portion, the more speed improvement you’ll get running it on a HPC system across multiple cores
Real-World Examples
Perfectly Parallel
- Image processing on multiple files
- Monte Carlo simulations
- Parameter sweeps
- Independent calculations
Imperfectly Parallel
- Weather modeling
- Fluid dynamics simulations
- Machine learning training
- Molecular dynamics
Next Steps
Understanding parallelization theory and Amdahl’s Law

HPC1: Introduction to High Performance Computing | University of Leeds