Synchronizing: Local & GitHub#
To sync a local repository with a GitHub repository you need two repositories (one local and one online) and then set up a link between them. The two possible paths are:
Local –> GitHub
Have a local git repository (which you started with
git init).Have an empty repository on GitHub.
Make the GitHub repository a remote for the local repository.
$ git remote add origin https://github.com/...The name
originis a local nickname for your remote repository.
GitHub –> Local
Have a repository on GitHub.
Clone the GitHub repository in your local machine. (this will create a local repo)
$ git clone https://github.com/...git clone copies a remote repository to create a local repository with a remote called
originautomatically set up.
Finding the GitHub repo link#
Each repository has an unique address composed by
GitHub link
GitHub user name
GitHub repository name
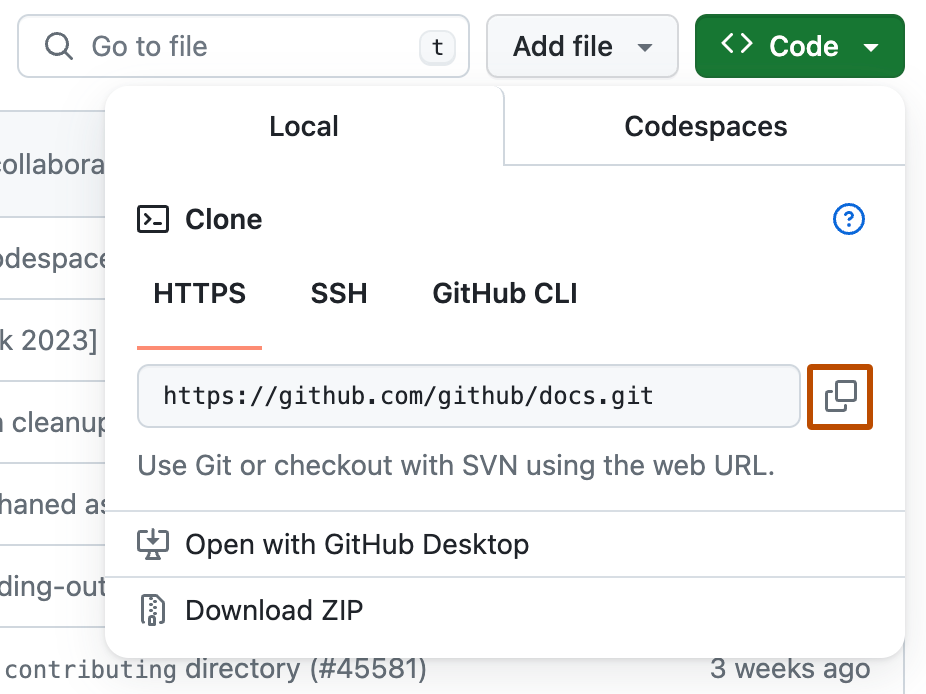
You can find the complete link in the main page of the repository, under the
code download green button (see image bellow)
Then, choose one of the tabs (HTTPS, SSH, or GitHub CLI) and copy the address:
Push local changes to a remote repo#
This command will push the changes (git commits) from our local repository to the repository on GitHub:
git push origin main
Note
You can push content to different branches, just change main for the desired
branch name in the above command
Pull remote changes to a local repo#
This command will pull changes from the remote repository to the local one:
git pull origin main
The “-u” flag#
Sometimes is useful to create a short for the git push origin main (or
git pull origin main). To do this, you need run one time the full command
with the -u flag:
git push -u origin main
After that, you can simple use git push or git pull without the origin main
arguments.
Please note that this works for the branch passed with the -u flag. If you want
to pull/push in other branches you should use the complete command.
A Basic Collaborative Workflow#
In practice, it is good to be sure that you have an updated version of the repository you are collaborating on, so you should git pull before making our changes. The basic collaborative workflow would be:
update your local repo with
git pull origin main,make your changes and stage them with
git add,commit your changes with
git commit -m, andupload the changes to GitHub with
git push origin main
Note
You can (and should) use other branches besides main.
