Tasks & Kanban#
When the project can be divided into tasks, it is convenient to manage the workflow using the Kanban method.
Definition
The term Kanban comes from Japanese and translates as “signal card”. Originally, Kanban was used in Toyota’s production facilities, where it also influenced agile development in IT and other departments. The aim is to establish a constant, orderly workflow. Moreover, Kanban can be combined with other agile methods such as Scrum.
- IONOS
Kanban can be used to managing workflow from the individual up to organizational level.
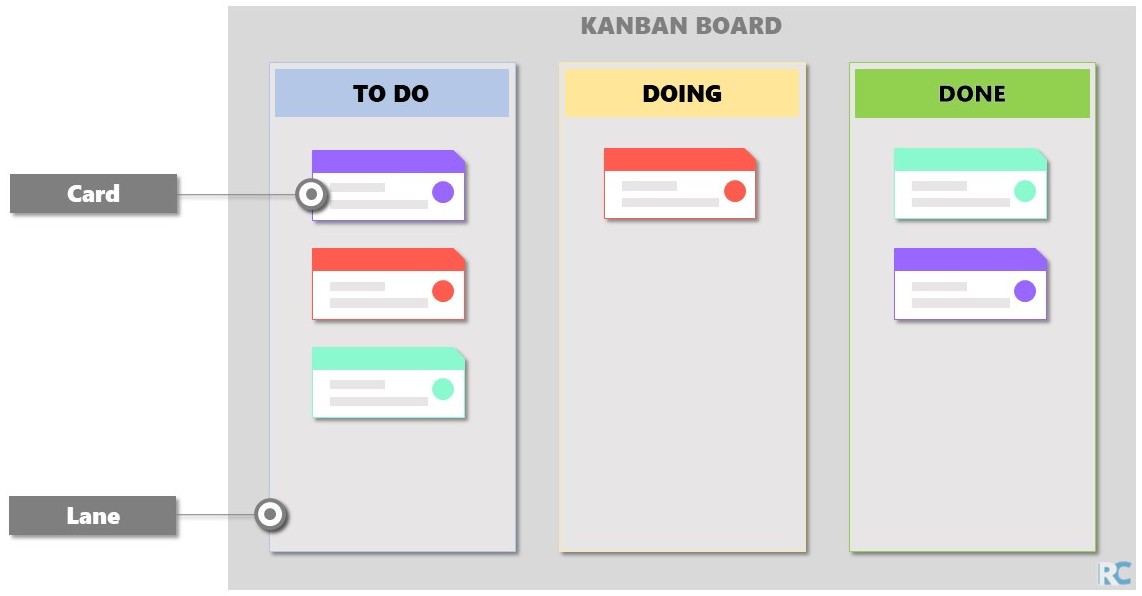
Simple Kanban Board#
The Kanban board helps to visualize and optimise the workflow. The board is organised through lanes (columns) and cards, where:
Lanes: defined steps
Cards: represent project tasks
By separating the cards in lanes it is easy to see the status of each task as well as the entire project workflow. See a simple Kanban board representation bellow:
Tip
Note that the in a Kanban board the task begins on the left side and as the task progresses through the execution steps, it is moved to the right lanes.
Useful Cards Content#
Title
Description
Attachments and links
Card type (usually distinguished by color)
Assignment
Card & comment history
Subtasks
Due date
Software Development: Useful Lanes#
Backlog (To Do: Unprioritized)
Ready (To Do: Prioritized)
Plan
Develop (Coding)
Testing
Pending Final Approval
Deployment
Done
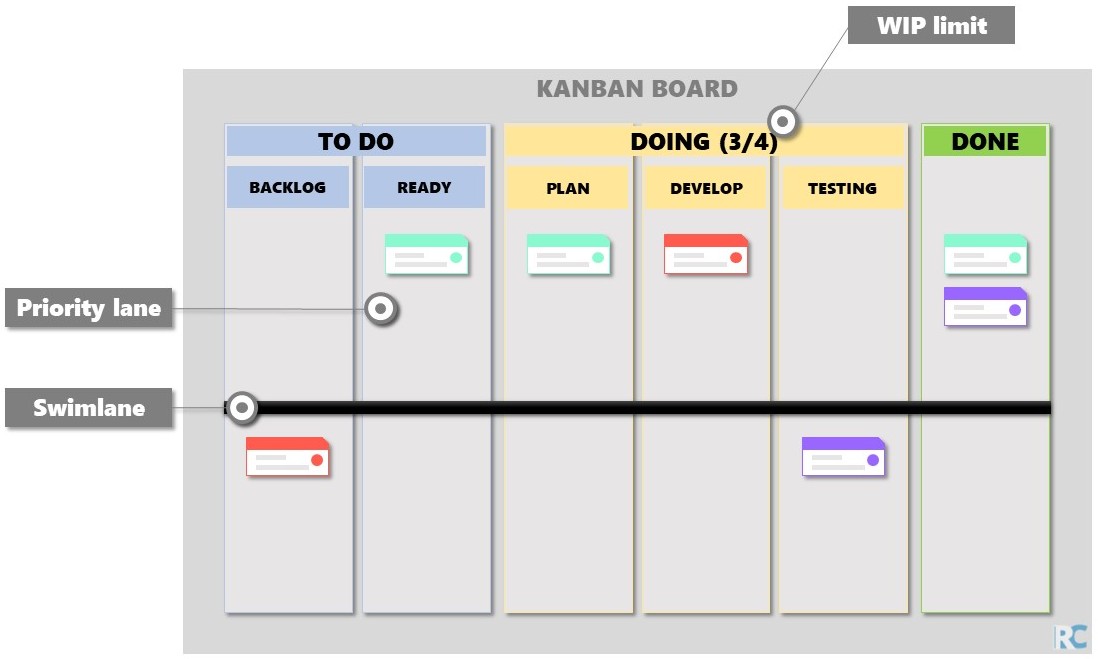
Useful Improvements#
Work-in-progress (WIP) limit: number of allowed open cards
Include more lanes
Priority lanes
Swimlanes: horizontal line to divide different groups
See a Kanban board with some improvements bellow:
Kanban: Pros & Cons#
Pros#
Easy integration
Increased visibility of the workflow
Improved delivery speed
Increased transparency
Cons#
absolutely necessary that the work can actually be divided into small steps
Trick#
The work-in-progress limits ensure that problems at a station quickly become visible and capacities can be reallocated accordingly. However, this is only possible if capacities can actually be swapped around. Team members must be able to work at different stations. Otherwise, blockages and overstraining will occur for some co-workers, while others will become idle – precisely the opposite of what Kanban is intended to achieve.
- IONOS
